We write the integers of A and B (in the order they are given) on two separate horizontal lines.
Now, we may draw connecting lines: a straight line connecting two numbers A[i] and B[j] such that:
A[i] == B[j];- The line we draw does not intersect any other connecting (non-horizontal) line.
Note that a connecting lines cannot intersect even at the endpoints: each number can only belong to one connecting line.
Return the maximum number of connecting lines we can draw in this way.
Example 1:
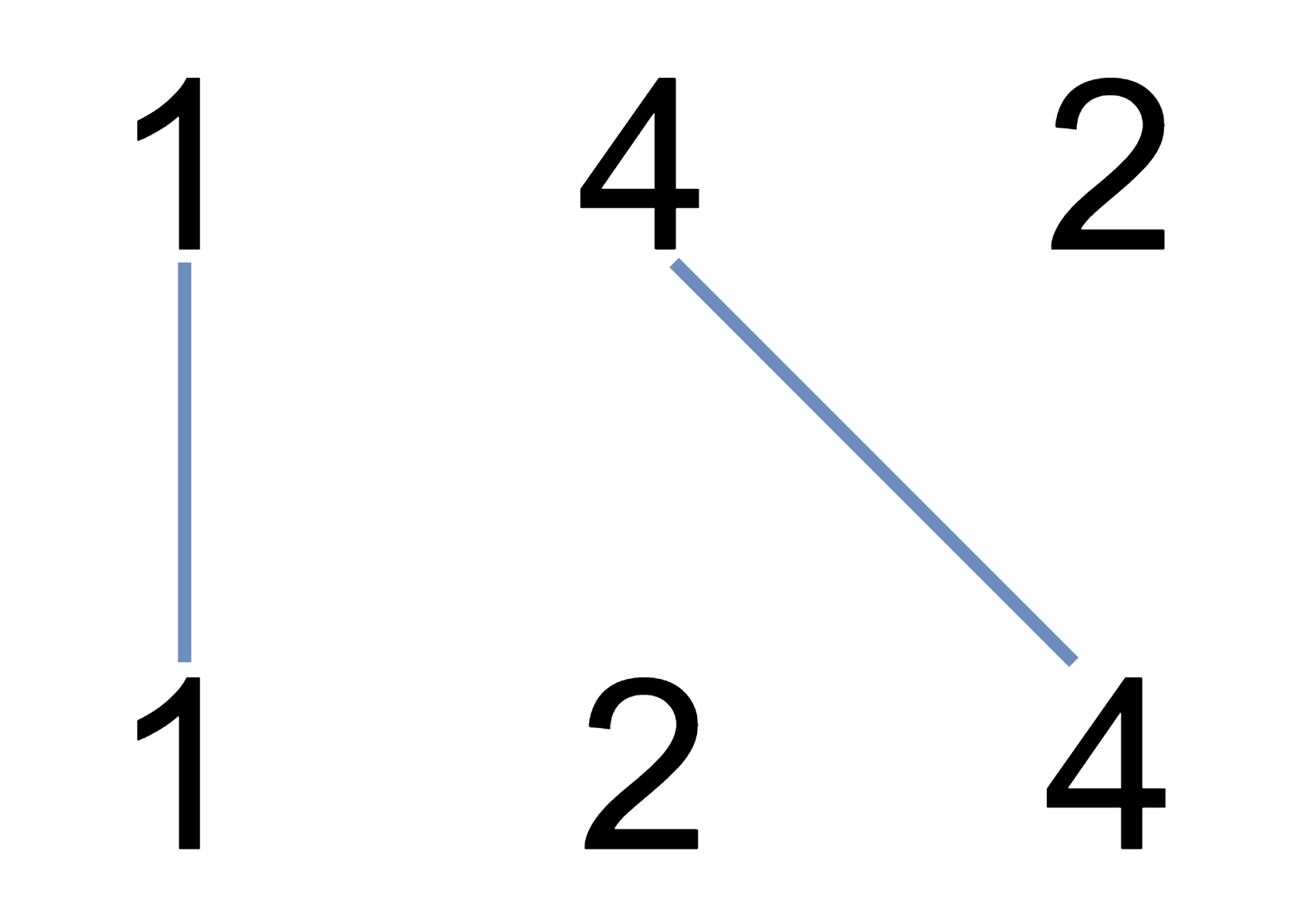
Input: A = [1,4,2], B = [1,2,4]
Output: 2
Explanation: We can draw 2 uncrossed lines as in the diagram.
We cannot draw 3 uncrossed lines, because the line from A[1]=4 to B[2]=4 will intersect the line from A[2]=2 to B[1]=2.
Example 2:
Input: A = [2,5,1,2,5], B = [10,5,2,1,5,2]
Output: 3
Example 3:
Input: A = [1,3,7,1,7,5], B = [1,9,2,5,1]
Output: 2
Solution
这个题采用动态规划的解法,先初始化dp数组全部为1, 然后初始化第一行和第一列,如果A[i] 中含B[0],那么在之后的dp[0][i]都初始化为1,因为这说明b[0]可以形成一条线,而且只有一条,同样的道理初始化dp的第一列。 然后从A和B的第二个元素开始调用动态规划转移方程: 如果A[i] == B[j],那么dp[i][j] = 1 + dp[i-1][j-1] 否则 dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1]
class Solution:
def maxUncrossedLines(self, A: List[int], B: List[int]) -> int:
dp=[[0 for i in range(len(A))] for j in range(len(B))]
if A[0] ==B[0]:
dp[0][0] = 1
for i in range(1,len(A)):
if B[0]==A[i]:
dp[0][i] =1
else:
dp[0][i]=dp[0][i-1]
for j in range(1,len(B)):
if B[j]==A[0]:
dp[j][0] =1
else:
dp[j][0] =dp[j-1][0]
for i in range(1,len(B)):
for j in range(1,len(A)):
if B[i]==A[j]:
dp[i][j] = 1+(dp[i-1][j-1])
else:
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1])
return dp[-1][-1]