Given two lists of closed intervals, each list of intervals is pairwise disjoint and in sorted order.
Return the intersection of these two interval lists.
(Formally, a closed interval [a, b] (with a <= b) denotes the set of real numbers x with a <= x <= b. The intersection of two closed intervals is a set of real numbers that is either empty, or can be represented as a closed interval. For example, the intersection of [1, 3] and [2, 4] is [2, 3].)
Example 1:
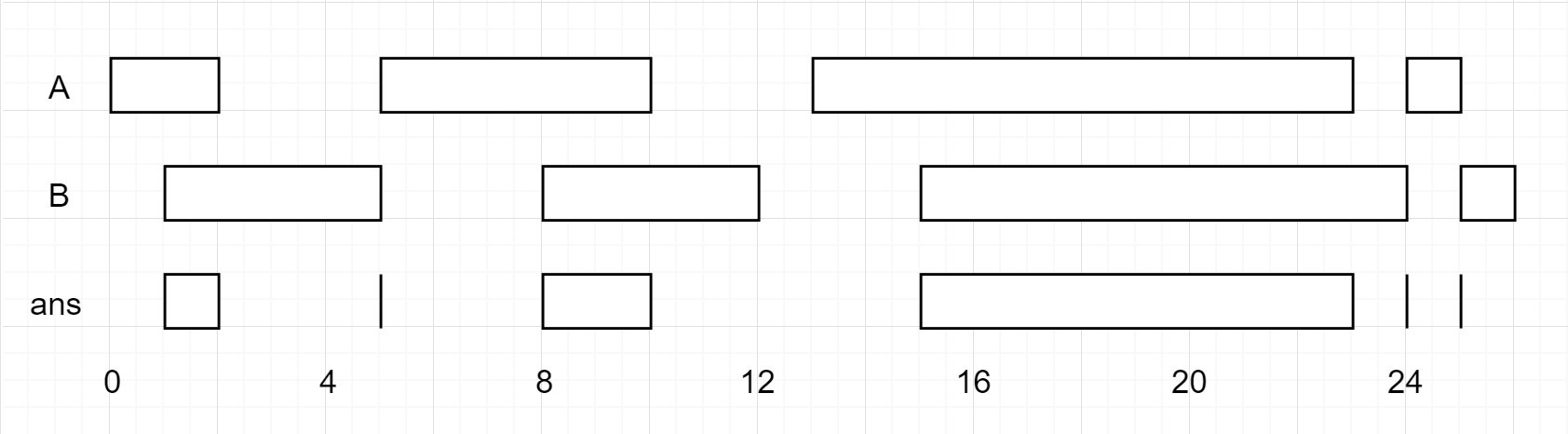
Input: A = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], B = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]]
Output: [[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]]
Reminder: The inputs and the desired output are lists of Interval objects, and not arrays or lists.
Solution
我们用两个指针分别指向2个list的第一个位置,如果没有交集,则把小的往前移。
class Solution:
def intervalIntersection(self, A: List[List[int]], B: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
i, j ,res = 0,0,[]
while (i<len(A) and (j<len(B))):
if (A[i][1]<B[j][0]):
i = i+1
elif (B[j][1] <A[i][0]):
j = j+1
else:
res.append([max(A[i][0],B[j][0]), min(A[i][1],B[j][1])])
if (A[i][1] <B[j][1]):
i = i+1
else:
j = j +1
return res
下面的视频具体解释了怎么移动和怎么比较。